Exploring the Cosmos: 30 Mind-Blowing Space Facts
Exploring the Wonders of Europe: 30 Fascinating Facts
The Power of Maternal Love: 30 Inspiring Facts About Moms and Kids
Discovering Deserts: 30 Fascinating Desert Facts
Church Chronicles: 30 Fascinating Facts About Sacred Spaces
Chronicles of Conflict: 30 Fascinating Facts About Wars Throughout History
Unlocking the Truth: 30 Fascinating Facts About Prisons
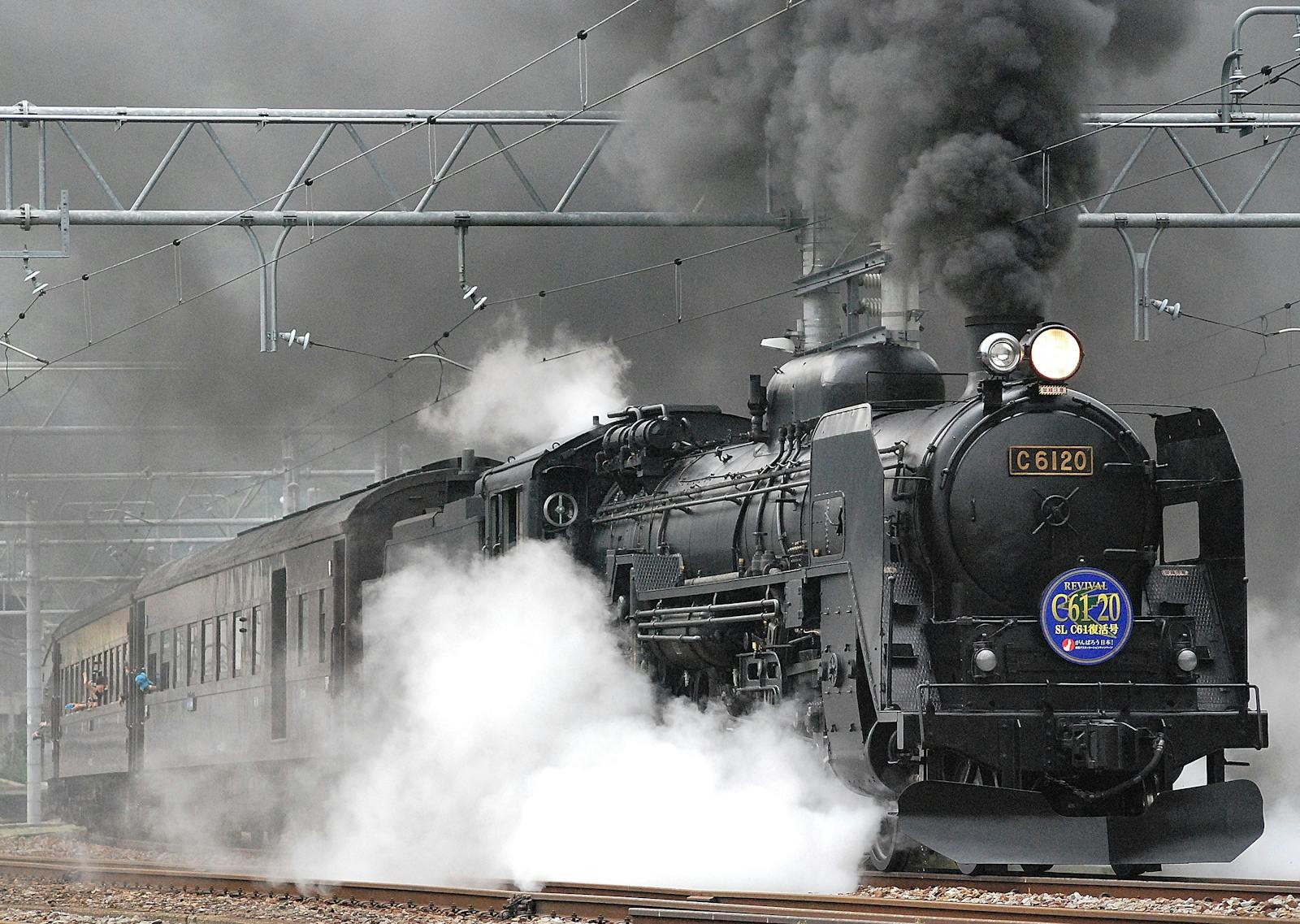
Railway Wonders: Exploring 30 Fascinating Train Facts
Dancing Through History: 30 Fascinating Facts About Dance
Beyond the Bark: Fun Facts to Know About Dogs!
Babies Unveiled: 30 Astonishing Facts About Infant Development
Botanical Wonders: 30 Fascinating Plant Facts
Discover the Wonders of the Human Body: 30 Fascinating Facts
Meowsterpieces: 30 Fascinating Facts About Cats
Beneath the Feathers: 30 Surprising Bird Facts Explored